LIGHTING BASICS
Lighting is measured by the
amount of luminous flux on a surface, called illuminance. It is expressed
either in foot-candles (illuminance in a square foot) or in lux (illuminance in
a square meter). An artificial light source is referred to as a lamp. Although
lamps are commonly identified by their wattage, this does not describe the
output of light. A watt is the measurement of energy consumption from a
particular light source. So an incandescent lamp and a fluorescent lamp can
have the same light output of foot-candles or lux while ranging dramatically
in wattage. As an example, a 60-watt incandescent lamp has the same light
output as a 15-watt fluorescent lamp.
Light coming from a single
point source can, like direct sunlight, create dark areas of shadow around the
pool of light it provides. A point source calls attention to the surface it is
illuminating and highlights its inherent characteristics. Diffuse light, like
that on a cloudy day, distributes light evenly and is not strong enough to create
shadows. While this even distribution of light may be good in a working
environment because it is easy on the eyes, it can seem a bit dull and lifeless
over time.
An unshaded lamp or poorly
positioned fixture with an exposed lamp can cause extreme brightness from a
light source called glare. While not measurable, glare is easily recognizable.
It can impair vision and induce discomfort as the eye usually squints to reduce
the impact of its harshness. Veiling reflection is another type of glare that is
caused by the brightness of
a light source reflecting
off a shiny surface such as glass. A familiar example might be the reflection
of a bright window on a computer screen. The well-thought-out distribution and
location of light fixtures can reduce glare significantly.
TYPES OF LAMPS
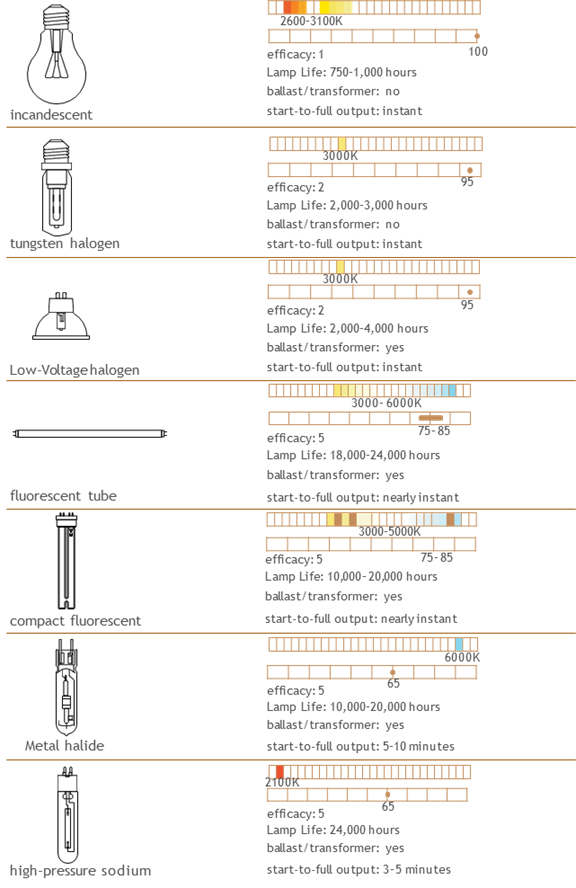
Many types of lamps are
available, each with specific characteristics for colour rendition, size, energy
consumption, and lamp life. Juggling all the variables can be complex. To
specify lamps correctly, designers should know their efficacy rating (1 = low/poor, 5 = high/excellent) as
well as their correlated colour temperature and colour rendering index.
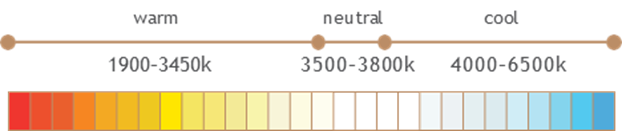
Correlated Color Temperature
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
NEW LIGHTING TECHNOLOGIES
Although fibre-optic and
LED lighting technologies have been around for a while, they are now becoming
more readily available to designers. Both lighting types are more energy-efficient than fluorescent lighting, but also much more cost-prohibitive. As
the market continues to focus on energy efficiency, however, designers will see
these technologies advance further and become more affordable.
Fibre-Optic Lighting
This technology relies on
strands of acrylic cables to transmit light from the light source, called the
illuminator, to the ends of the cables. The illuminator is simply a box with
either a tungsten halogen lamp or a metal halide lamp of varying wattages.
Tungsten halogen lamps are more common, while metal halide lamps are typically
used for large installations. The ends of the acrylic cable are gathered in a
bundle and placed in an aperture directly in front of the lamp. The
illuminators should be conveniently located for easy access to relamp the
fixtures. It is also important to note that the illuminators need ventilation
to release the heat that is generated by the lamp.
Depending on the lighting
design, there can be less than a handful of acrylic cables or hundreds of
cables. The length of the cables can vary per installation, but as a general
rule, they should not exceed 50 feet (15 meters) or light transmission will be
compromised. The advantage of this system is that multiple lights can be
located in difficult-to-access places, controlled by a single lamp inside the
illuminator.
LED Lighting
Although light-emitting diodes
(LEDs) use a fraction of the electricity and last up to ten times as long as
fluorescent lamps, they are too costly for use in general lighting. LEDs are
available in high intensities of red, green, and blue light, and the
combination of all three coloured lights
Comparative Correlated Color Temperature
yields white light. Varying
combinations of the three colours can produce a full spectrum of colour options.
LEDs have the additional advantage of producing no heat. Currently, LEDs are
used in interior design to create desired effects such as accenting a reveal or
washing a wall with coloured light. As the technology advances, it will become
more affordable and eventually be applied to general-purpose lighting.
LIGHTING TERMINOLOGY
Ballast: a small device that controls the flow of current by providing the required
starting voltage and then reducing the current during operation.
Correlated
Colour Temperature (CCT): spectral characteristic of a light
source, measured in Kelvins (K). The lower the temperature, the warmer the
(yellow/red) tones; the higher the temperature, the cooler the (blue) tones.
sunlight at dawn has a colour temperature of 1900K while a uniform overcast sky
is 6527K.
Colour
Rendering Index (CRI): scale from 1 to 100 that describes the
effect of a light source on an object or surface. The higher the index, the
more natural and vibrant the object appears.
Dimming
Ballast: Device used with fluorescent lamps to vary the output
of light by the use of a dimmer control.
Efficacy,
or Luminous Efficacy: Efficiency in which electrical power is
converted to light. Efficacy measures the number of lumens emitted per watts
consumed (lm/W).
Low-voltage
Lamp: Incandescent lamp that operates with low voltage,
ranging from 6 to 12 volts.
Luminance:
Amount of light reflected or transmitted by an object.
Transformer: The device designed to raise or lower electric voltage.
If you find
This information is helpful, please share it.
Thanks! For reading the article.








No comments:
Post a Comment